Did you know that sharp-tailed snakes have a surprisingly diverse diet? These fascinating reptiles, found in various regions of the United States, have a wide range of eating habits that contribute to their survival and well-being.
Sharp-tailed snakes primarily feed on slugs and their eggs, which constitute the bulk of their diet. They may also consume other soft-bodied invertebrates like earthworms and insect larvae. These snakes are particularly adapted to hunting in moist environments where their prey is abundant, using their sharp tail tip to help maneuver and secure their food.
In this article, we will explore the eating habits of sharptailed snakes, their primary food sources, and the techniques they use to capture their prey.
Key Takeaways:
- Sharp-tailed snakes have a diverse diet, ranging from small invertebrates to other snakes.
- Understanding their eating habits and food sources is crucial for their conservation.
- Sharp-tailed snakes use various techniques to capture and consume their prey.
- Their diet can be influenced by factors such as habitat, prey availability, and nutritional needs.
- Managing their diet in captivity presents unique challenges.
Overview of Sharp-tailed Snakes
Before we delve into the diet of sharp-tailed snakes, let’s take a moment to familiarize ourselves with these fascinating reptiles.
Sharp-tailed snakes, also known as contia tenuis, can be found in various regions of the United States.
They belong to the Colubridae family and are known for their slender bodies and distinctive tail tip, which gives them their name.
Species Description and Identification
Sharp-tailed snakes have a unique appearance that sets them apart from other snake species.
They typically measure between 8 to 14 inches in length, with females being slightly larger than males.
Their coloration varies, but they commonly have a combination of brown, gray, or black scales.
One distinguishing feature of sharp-tailed snakes is the row of scales on their ventral side that resemble a keeled edge.
To identify a sharp-tailed snake, look for these key characteristics:
- A slender body with smooth scales
- A pointed tail tip
- A row of keeled scales on the ventral side
Habitat and Distribution
Sharp-tailed snakes are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and even suburban areas.
They are primarily terrestrial but are also known to climb trees and shrubs. These snakes prefer areas with moist soil and ample ground cover, such as leaf litter or fallen logs.
As for their distribution, sharptailed snakes can be found in different regions of the United States, including the Pacific Northwest, the Rocky Mountains, and parts of the Midwest.
Their range extends from British Columbia, Canada, down to California and east to Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Dietary Habits of Sharp-tailed Snakes

Sharp-tailed snakes have unique dietary habits that play a vital role in their survival.
Understanding the primary diet composition of these snakes sheds light on their food preferences and hunting techniques.
Let’s dive into the intriguing world of sharptailed snake’s feeding behavior.
Primary Diet Composition
The primary diet of sharp-tailed snakes consists of a variety of prey items found in their natural habitat.
These snakes are opportunistic hunters and have a diverse menu that includes small mammals, such as voles and mice, as well as amphibians, lizards, and occasionally small birds.
Their ability to adapt their diet allows them to thrive in different environments.
When it comes to feeding behavior, sharptailed snakes are adept at capturing their prey.
They use a combination of stealth and ambush tactics to secure their meal.
These snakes rely on their excellent camouflage and exceptional hunting skills to blend in with their surroundings and surprise their unsuspecting prey.
Hunting Techniques and Feeding Behavior
Sharp-tailed snakes employ various hunting techniques to capture their prey effectively.
They are known to use a combination of both active pursuit and sit-and-wait strategies.
During active pursuit, sharptailed snakes actively search for their prey by slithering through their habitat while using their keen senses, such as their sense of smell and vision, to detect potential food sources.
Once they spot their prey, these snakes quickly strike and immobilize it using their venomous bite.
On the other hand, when utilizing the sit-and-wait strategy, sharptailed snakes patiently wait for their prey to come within striking distance.
They position themselves strategically, often near areas frequented by their preferred food sources, and rely on their camouflage to blend in with the environment.
When an unsuspecting prey item comes close enough, the snake makes a rapid and precise strike to capture its meal.
By employing a combination of these hunting techniques and feeding behavior, sharptailed snakes are well-equipped to secure the necessary nourishment for their survival.
Impact of Habitat on Diet

The habitat in which sharp-tailed snakes reside plays a crucial role in shaping their diet.
The availability of prey in different habitats directly influences the food sources of these reptiles.
As their habitat changes, so does their prey selection, leading to variations in their diet.
Availability of Prey in Different Habitats
Sharp-tailed snakes adapt to various habitats, including grasslands, wetlands, forests, and deserts.
Each habitat provides a unique range of prey species for these snakes to feed on. For example, in grassland habitats, they may primarily consume small rodents and insects, while in wetland environments, their diet may consist of amphibians and fish.
The diverse prey availability in different habitats enables sharptailed snakes to adjust their diet according to the resources present.
This adaptability ensures their survival and allows them to meet their nutritional needs.
Seasonal Changes in Diet
The diet of sharp-tailed snakes can also be influenced by seasonal changes. As the environment experiences shifts in temperature and prey availability, these snakes may alter their feeding habits to adapt.
During warmer months, when prey populations are abundant, sharptailed snakes may consume a wider variety of food sources.
In contrast, during cooler months or periods of low prey availability, they may rely on a more limited range of prey items to sustain themselves.
These seasonal changes in diet reflect the dynamic nature of sharp-tailed snakes’ feeding behavior and their ability to optimize their food consumption based on environmental conditions.
By understanding the impact of habitat on the diet of sharptailed snakes, we gain valuable insights into the ecological dynamics of these reptiles.
This knowledge can aid in their conservation efforts and help guide habitat management strategies that support their dietary needs.
To learn more about sharp-tailed snakes and their habitat requirements, you can refer to this detailed brochure provided by the government of British Columbia.
Nutritional Needs and Diet Management
When it comes to keeping sharp-tailed snakes in captivity, understanding their nutritional needs is essential for their overall health and well-being.
In this section, we will explore the specific nutritional requirements of these fascinating reptiles and address the challenges in diet management that can arise.
Nutritional Requirements
Sharp-tailed snakes have unique nutritional requirements that must be met in order for them to thrive in captivity.
Their diet primarily consists of small rodents, insects, and other invertebrates. These prey items provide the essential nutrients, such as proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, that sharptailed snakes need to maintain their health.
When keeping sharp-tailed snakes in captivity, it is important to provide them with a balanced and varied diet that closely mimics their natural prey.
This can include offering a combination of frozen-thawed rodents, live insects, and commercially available reptile diets that are specifically formulated for snakes.
One study on the nutritional needs of sharptailed snakes found that a diet consisting of 60-70% rodents, 20-30% insects, and 5-10% reptile diets provided the optimal balance of nutrients for these reptiles.
Challenges in Captivity
Managing the diet of sharp-tailed snakes in captivity can be challenging due to several factors.
One of the main challenges is ensuring that the snakes receive a variety of prey items to meet their nutritional needs.
It can be difficult to obtain a consistent supply of live insects, and providing a diverse range of frozen-thawed rodents may also be challenging.
Additionally, some sharptailed snakes may be reluctant to accept non-live prey or may have specific dietary preferences.
This can make it necessary for snake keepers to experiment with different food items and feeding techniques to ensure their snakes are getting the nutrients they need.
Another challenge in diet management is monitoring the snakes’ feeding behavior and adjusting their diet accordingly.
Some snakes may have specific feeding schedules or may go through periods of reduced appetite, which can affect their overall nutritional intake.
Regular monitoring and consultation with a reptile veterinarian can help ensure that the snakes’ diet is appropriately managed.
Overall, understanding the nutritional needs of sharp-tailed snakes and addressing the challenges of diet management in captivity are key to providing them with a healthy and balanced diet.
By meeting their specific nutritional requirements, snake keepers can help promote the well-being and longevity of these fascinating reptiles.
Conservation Status and Dietary Implications

As we have explored the dietary habits of sharp-tailed snakes, it becomes clear that their food sources have direct implications for their conservation status.
The survival and well-being of these reptiles are closely tied to the availability and quality of their natural food sources.
Threats to Natural Food Sources
Unfortunately, sharp-tailed snakes face several threats to their food sources, which are critical for their survival.
Habitat loss and degradation due to human activities, such as urban development and agriculture, can lead to the destruction of the ecosystems these snakes rely on for their prey.
The decline in suitable habitats can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems and have cascading effects on the availability of food for these snakes.
Invasive species are another significant threat to the sharptailed snake’s food sources.
Non-native species can outcompete or prey upon the native species that these snakes rely on as their main food source.
This can lead to a reduction in the availability of suitable prey for sharptailed snakes, potentially impacting their population numbers and overall health.
Conservation Efforts Related to Diet
Conservation efforts focused on managing the diet and preserving the habitats of sharp-tailed snakes play a crucial role in their long-term survival.
By understanding their dietary habits and the threats they face, conservationists can develop strategies to protect and restore their natural food sources.
Habitat conservation and restoration initiatives aim to create and maintain suitable habitats for sharp-tailed snakes and their prey.
This includes protecting important breeding and foraging grounds, as well as implementing measures to mitigate habitat loss and degradation.
By preserving the ecosystems that support their food sources, we can ensure a sustainable future for these reptiles.
Additionally, efforts to control and eradicate invasive species are essential for safeguarding the food sources of sharptailed snakes.
Identifying and removing non-native species that pose a threat to native wildlife can help restore balance to ecosystems and promote the availability of suitable prey for these snakes.
Education and public awareness campaigns also play a vital role in conservation efforts related to the diet of sharptailed snakes.
By educating the public about the importance of preserving habitats and protecting native wildlife, we can foster a greater understanding and appreciation for these reptiles and their role in ecosystems.
Research and Studies on Sharp-tailed Snakes
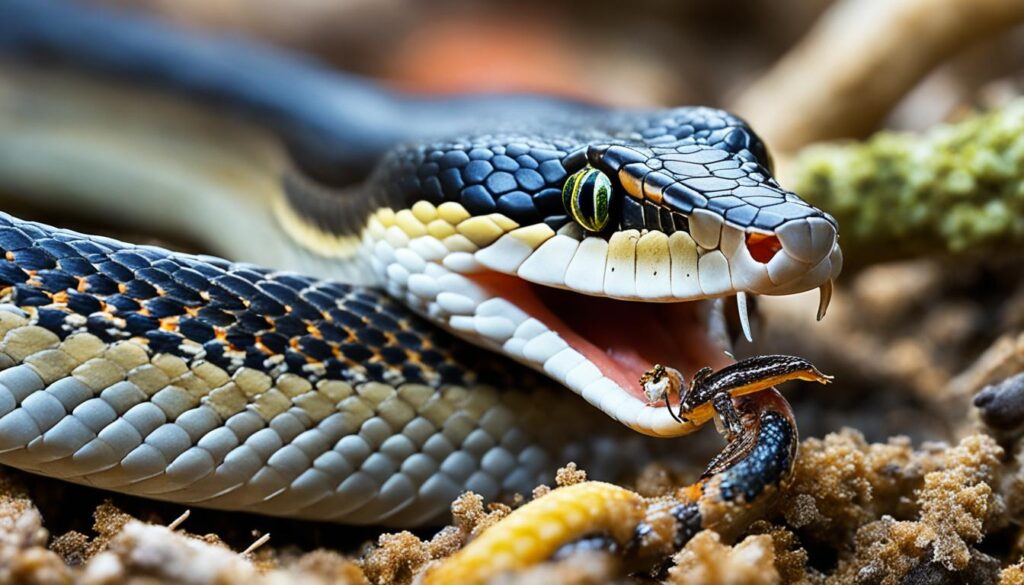

Scientists and researchers have conducted extensive research and studies on sharp-tailed snakes to deepen our understanding of their fascinating biology, including their diet.
By delving into the intricacies of their feeding habits, these scientific investigations have shed light on various aspects of their ecological role and behavior.
Recent Scientific Findings
Recent scientific findings have uncovered valuable insights into the diet of sharp-tailed snakes.
Through careful observation and meticulous research, scientists have identified the range of food sources that these snakes rely upon for sustenance.
For example, studies have revealed that sharp-tailed snakes primarily feed on small prey such as insects, arthropods, and worms.
These scientific discoveries have provided a better understanding of the specific dietary preferences and nutritional requirements of these reptiles.
In addition to unveiling their primary food sources, recent research has also uncovered interesting details about the hunting strategies employed by sharp-tailed snakes.
For instance, scientific findings have demonstrated that these snakes use a combination of ambush and pursuit techniques to capture their prey.
This research has provided valuable insights into the hunting techniques and feeding behavior of sharp-tailed snakes in their natural habitats.
Gaps in Current Knowledge
While there have been significant advancements in understanding the diet of sharp-tailed snakes, there are still gaps in current knowledge that require further investigation.
These gaps present exciting opportunities for future research to unravel the intricacies of these snakes’ feeding habits.
For instance, there is a need to explore the impact of environmental factors, such as habitat changes and prey availability, on the dietary patterns of sharp-tailed snakes.
Additionally, more in-depth studies are required to examine the potential variations in their diet across different geographical regions.
By addressing these gaps in knowledge through systematic research and scientific studies, we can enhance our understanding of the ecology and biology of sharp-tailed snakes.
This knowledge will not only contribute to the conservation efforts for these remarkable reptiles but also provide insights into the intricate dynamics of predator-prey interactions within their ecosystems.
If you’d like to learn more about sharp-tailed snakes, consider visiting this informative resource for comprehensive information on these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diet of sharp-tailed snakes is influenced by several factors, including their habitat, prey availability, and nutritional requirements.
Understanding their dietary habits is crucial for their conservation and proper care, whether in their natural environments or in captivity.
By exploring the various aspects of their diet, we can gain a deeper appreciation for these fascinating reptiles and contribute to their well-being.
Sharp-tailed snakes have specific dietary preferences, with their primary food sources consisting of small rodents, insects, spiders, and occasionally other snakes.
These snakes employ various hunting techniques and feeding behaviors to locate and capture their prey.
The availability of suitable habitats and prey in different regions plays a significant role in shaping their diet.
For those who keep sharp-tailed snakes in captivity, understanding their nutritional needs is essential for maintaining their health and vitality.
Providing a well-balanced diet that meets their specific requirements is crucial for their overall well-being.
However, managing their diet in a captive setting can present challenges, requiring careful consideration of portion sizes and the inclusion of the necessary nutrients.
Efforts to conserve sharp-tailed snakes and protect their natural habitats also involve understanding and managing their diet.
Threats to their food sources, such as habitat loss or the decline of prey populations, can have severe implications for their survival.
Conservation efforts include implementing strategies to mitigate these threats, promoting sustainable land management practices, and raising awareness about the importance of preserving their habitats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How rare are sharp-tailed snakes?
Sharp-tailed snakes are considered relatively uncommon. Their elusive nature and preference for specific habitats, typically moist environments under rocks and logs, make them less frequently encountered than other snakes.
Q: Are common sharp-tailed snakes poisonous?
No, common sharp-tailed snakes are not poisonous. They are harmless to humans and rely on their ability to burrow and hide to avoid predators rather than venom for protection.
Q: Do sharp-tailed snakes hibernate?
Yes, sharp-tailed snakes do hibernate. They typically enter a state of brumation (a form of hibernation for reptiles) during the colder months, often congregating in communal nests to retain warmth.
Q: How big do sharp-tailed snakes get?
A: Sharp-tailed snakes are relatively small; they typically grow to about 12 to 18 inches in length, making them one of the smaller snake species found in their native habitats.
Q: Do sharp-tailed snakes bite?
Sharp-tailed snakes can bite if threatened or handled, but their bites are harmless to humans. They are non-venomous and their small size makes them less daunting than other snake species.
Q: What do sharp-tailed snakes eat in California?
In California, sharp-tailed snakes primarily feed on slugs and their eggs. They may also occasionally eat other soft-bodied insects and larvae.




